Causes and Prevention Methods of Defects in casting chains
 Aug 10, 2022|
Aug 10, 2022| View:1834
View:18341. Slag pocket
Features: The slag pockets are the holes inside the surface of the casting, which are round, oval, or irregular. Sometimes multiple slag pockets form an air mass, and the subcutaneous is generally pear-shaped.
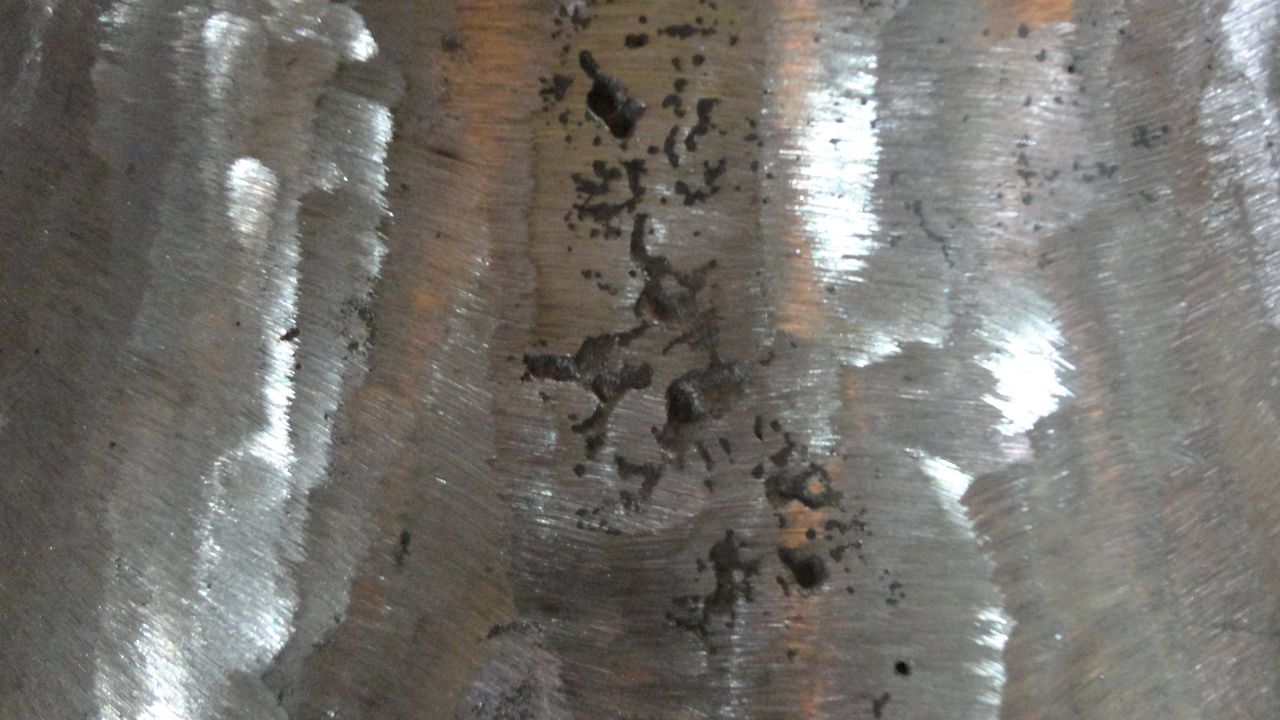

Formation reasons:
(1) The preheating temperature of the mold is too low, and the liquid metal cools too fast when passing through the gating system.
(2) The exhaust design of the mold is poor, and the gas cannot be discharged smoothly.
(3) The paint volatilizes or decomposes gas, resulting in stomata.
(4) There are holes and pits on the surface of the mold cavity. After the liquid metal is injected, the gas in the holes and pits rapidly expands and compresses the liquid metal to form a choke hole.
(5) The surface of the mold cavity is rusted and not cleaned.
(6) The raw materials (sand cores) are stored improperly and are not preheated before use.
(7) The deoxidizer is not good, or the amount is not enough or the operation is improper.
Prevention method:
(1) The mold should be fully preheated, the particle size of the painting (graphite) should not be too fine, and the air permeability should be good.
(2) Use sloped pour.
(3) Raw materials should be stored in a ventilated and dry place and should be preheated when used.
(4) Choose a deoxidizer (Mg) with a better deoxidation effect.
(5) Pouring temperature should not be too high.
2. Shrinkage
Features: Shrinkage cavity is a kind of rough surface existing on the surface or inside of the casting. A slight shrinkage cavity is many scattered small shrinkage cavities, that is, shrinkage porosity and the grains at the shrinkage cavity or shrinkage porosity are coarse. It often occurs near the runner in the casting, the root of the riser, the thick part, the thickness transition of the wall and the thick part with a large plane.

Formation reasons:
(1) The temperature control of the mold does not meet the requirements of directional solidification.
(2) Improper selection of paintings, poor control of painting layer thickness in different parts.
(3) The position of the casting in the mold is not properly designed.
(4) The pouring temperature is too low or too high.
Prevention method:
(1) Increase the temperature of the abrasive tool.
(2) Adjust the thickness of the coating layer, the coating should be sprayed evenly.
(3) Partially heat the mold or use thermal insulation material to locally keep it warm.
(4) Place a copper block at the hot joint to chill the part.
(5) Design heat sinks on the mold, spray water outside the mold, or accelerate the cooling speed.
(6) Design a pressure device on the mold riser.
(7) Select an appropriate pouring temperature, and make sure the design of the pouring system also should be accurate.
3. Slag blowhole(Flux or metal oxide inclusion slag)
Features: Slag holes are distributed on the surface or inside of the casting, all or part of the holes are filled with slag, and the shape is irregular. It is difficult to find the dotted solvent slag, after removing the slag, it will appear smooth holes, which are distributed in the lower part of the pouring position, near the inner runner or at the dead corner of the casting. Oxide slags are mostly distributed on the surface of the casting near the inner runner. These slags usually come in flakes, broken from the interlayer, and the oxide is in it, which is one of the sources of crack formation in the casting.
Formation reasons: slag holes are mainly caused by the alloy smelting process and pouring process(including incorrect design of the pouring system), the mold itself will not cause slag holes, and the metal mold is one of the effective methods to avoid slag holes.
Prevention method:
(1) Set a correct pouring system or use a cast fiber filter.
(2) Adopt inclined pouring method.
(3) Strictly control the flux quality.
4. Cracks (hot cracks, cold cracks)
Features: the appearance of the crack is straight line or irregular curve. The hot crack surface is strongly oxidized to dark gray or black. The surface of the cold crack is clean and has metallic luster. Generally, the outer crack can be found directly, while the inner can only be seen by other methods. Cracks are often related to shrinkage and slag holes.

Formation reasons: the metal mold casting is prone to crack, because the mold itself has no concession, and the cooling speed is fast, it is easy to cause the internal stress of the casting to increase. When the opening is too early or too late, the pouring angle is too small or too large, the coating layer is too thin, etc. It is easy to cause cracks.
Prevention method:
(1) Pay attention to the casting structure, make sure the uneven thickness parts transitioned evenly, adopt an appropriate fillet size.
(2) Adjust the coating thickness to make each part of the casting reach the required cooling rate to avoid the formation of internal stress.
(3) Pay attention to the working temperature of the mold, adjust the mold slope, and timely take out the casting and cool it slowly.
5. Cold shut(poor fusion)
Features: cold shut is a kind of surface crack with open seams or round edges, its middle is separated by oxide skin, and is not completely integrated. When the cold shut is serious, it becomes undercasting. Cold shut often occurs on the top wall of the casting, on thin horizontal or vertical surfaces, at the junction of thick and thin walls, or on thin support plates.

Formation reasons:
(1) The exhaust design of the mold is unreasonable.
(2) The working temperature is too low.
(3) The paint quality is bad(artificial, material).
(4) The pouring speed is too slow, etc.
Prevention method:
(1) Design the correct runner and exhaust system.
(2) For large-area thin-walled castings, the coating should thicken to conductive to molding.
(3) Properly increase the mold working temperature.
(4) Adopt inclined pouring method.
6. Blowhole
Features: relatively regular holes are formed on the surface or inside of the casting, the shape of which is consistent with sand grains.
Formation reasons:
Blowholes are formed when the sand falling from the sand core is wrapped by the liquid and exist on the surface of the casting.
(1) The surface strength of the sand core is bad, and it is burnt or not fully cured.
(2) The size of the sand core does not match the mold, when the mold is closed the sand core is crushed.
(3) The mold is contaminated with sand.
Prevention method:
(1) Strictly control the sand core produce process and check the quality.
(2) The sand core is consistent with the size of the outer mold.
(3) Blow out the sand in the mold cavity when placing the sand core.